The self-driving race in China is heating up. Search giant Baidu announced a series of significant progress in the development of its autonomous driving ecosystem at the Baidu Create 2019, its annual conference on artificial intelligence in Beijing this week.
The key behind the progress is the millions of test miles the company has completed, said Li Zhenyu, Baidu's vice president and general manager of its Intelligent Driving Group. He announced that Baidu’s fleet of 300 autonomous vehicles have been put into test across 13 cities, and have by far driven over 2 million kilometers or 1.24 million miles on urban road tests.
Those miles were achieved under L4, a high level of self-driving system that is capable of handling the car under most situations, including turning and pedal control, as well as reacting to mechanical malfunctioning and aggressive driving, according to the Society of Automotive Engineers International.
Earlier this week, Baidu was granted T4 licenses by Beijing transportation authorities to test self-driving cars on urban roads in the capital city, making the company the first to have received this highest-level permit issued so far in China. The “T” is Chinese government’s own definition of self-driving levels, in which T4 represents the ability to complete complex maneuvers including U-turn, passing and parallel parking.
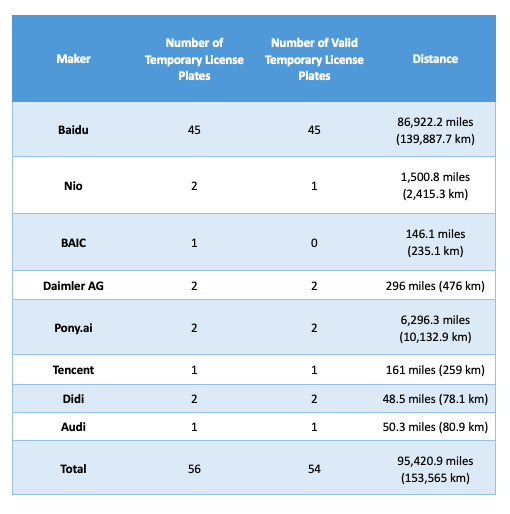
Back in April this year, authorities released a long-waited report detailing self-driving test activities in Beijing. The report showed that Baidu had tested 45 autonomous vehicles which accounted for more than 90 percent of the total distance travelled by autonomous cars in the road test in Beijing last year. Following Baidu was Pony.ai (小马智行), a self-driving technology startup founded by two former top engineers at Baidu, with two cars tested and 6,300 miles driven. Electric vehicle startup NIO came third with two cars and 1,500 miles.

Li also announced that “Apolong”, an autonomous minibus program developed with Baidu’s open source self-driving platform Apollo in partnership with Chinese carmaker King Long (金龙) has so far served around 40,000 passengers in 25 Chinese cities. The minibus can serve up to 14 passengers. At Baidu Create 2018 in July last year, Baidu announced that it has started mass production of the Apolong minibuses at King Long’s factory in Xiamen, in southeastern China’s Fujian Province.
Other highlights at the AI conference this year include the latest enhancements made to Apollo. Baidu releases the 5.0 version of the open source platform with a slew of upgrades from previous one, with 17 core capabilities enhanced and its data pipeline finally accessible to developers. With Apollo 5.0, self-driving developers can now complete dynamic calibration for a vehicle in just 30 minutes through cloud computing.
With the platform now supporting T4, many new use cases are now achievable with self-driving technology as well. For example, Baidu announced a valet parking solution, utilizing on-car machine learning to search for parking spaces and perform automated valet parking.
According to Baidu, the number of developers who have downloaded Apollo’s codes from the project’s GitHub page has reached 12,000, up 20% from a year ago. The open source platform was launched in 2017.

The company also revealed a plan to launch the “Apollo Go” robo-taxi program in the city of Changsha that will serve as the pilot zone. Under the program, 5G network and an intelligent upgrade of roadway infrastructure will be deployed to support Baidu’s level 4 autonomous driving taxi fleet. The program will be available to customers later this year, when they can call a ride via the Apollo Go smartphone app.
At the conference, Baidu claimed that it’s robo-taxi fleet will be the country's largest Level 4 self-driving taxi fleet, with 45 cars. Changsha issued 49 licenses for test vehicles in total.
Baidu began work on autonomous cars around 2016 when CEO Robin Li decided to shift the company’s focus into artificial intelligence, giving Baidu an advantage in AI sectors compared to many other top-tier internet companies.
Speaking at the Baidu Create 2019, Li zhenyu said Apollo has teamed up with 156 partners that include car manufacturers, parts suppliers and other car allies. Notable collaborators include Chinese manufacturers Geely, Great Wall Motors, BYD, as well as international carmakers such as Volvo and Ford.
Despite taking the lead in the self-driving testing race, Baidu is facing serious challenges from local competitors such as Pony.ai, Didi Chuxing.
Chinese ride-hailing company Didi Chuxing, which is dominating the market after it acquired Uber’s China operation in 2016, said that it has set up fleets of dozens of self-driving vehicles and launched road test in several cities in China. “With more than 550 million registered users and enormous data, Didi’s ride-sharing business will provide one of the most applicable commercial solutions for autonomous-driving technology over the next 10 years,” co-founder and CTO Zhang Bo told Caixin (paywall).
Other internet giants have also joined the fight to capture the emerging market. Alibaba said last year that it has been conducting self-driving vehicle tests, while the Chinese e-commerce giant has been looking to hire 50 more self-driving specialist for its AI research lab.
In September 2018, Chinese authorities have given permission for Alibaba to test its autonomous vehicles in genuine conditions on public roads in Hangzhou, where the company is headquartered.