The long-awaited Beijing Autonomous Driving Report for 2018 is finally released on April 1, 2019. According to the report, which is prepared by the regulating body Beijing Automated Driving Test Management Joint Working Group, temporary license plates were granted to 56 self-driving vehicles, which had covered over 95,000 miles or 153,600 kilometers during the past year.
Eight major internet companies and car OEMs received these temporary license plates: Baidu, NIO, BAIC , Pony.ai, Tencent, Didi, Daimler and Audi. The two types of companies, split in half in terms of number, also represent where the major participants come from to engage in the latest trend of self driving in China.
Report Summary: Who's the winner?
The core information of the report is summarized below in a table. Baidu is the indisputable leader for the search giant that obtained the majority of the license plates issued. During the past year, Baidu’s self driving cars have covered over 86,922 miles, representing 91% of the total distance covered by all companies.
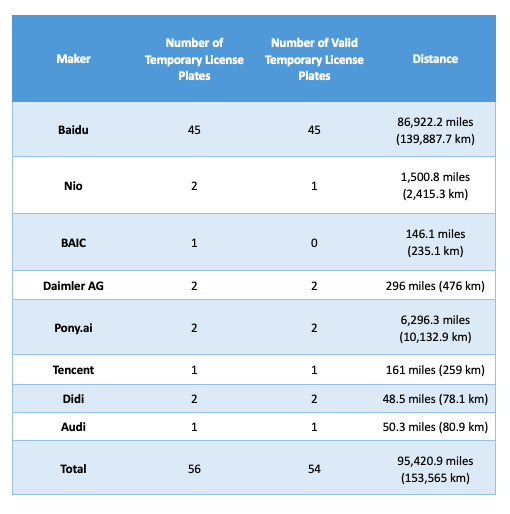
Other participants each has one or two plates, but their distance covered varies. The only self driving car valid for road test from NIO, a startup company selling electric SUVs, accumulated 1500 miles, while Audi only have 50 miles on the test record with 2 cars.
The issuing time of the plates also has a significant effect on miles traveled, since a number of vehicles from various companies were issued plates near the end of 2018. For example, 20 of Baidu's self driving vehicles were issued plates on December 25, 2018. Thus, the majority of the miles covered was accomplished by the other 25 vehicles.
Given this, the average distance covered per vehicle by Baidu is 86,922.2 / 25 = 3477 miles. NIO's was 1500 miles, for it only had one car valid for testing. Pony.ai's was 3148 miles. Others' are even lower. Therefore, in terms of average distance covered per vehicle, Baidu is still the winner.
Why Beijing? Aren't we talking about China?
While Beijing cannot represent the country as a whole, the capitol city is indeed the main testing ground of China.
This is due to the fact that firstly, more than half of all the self driving test licenses came from Beijing; Secondly, Beijing has more public roads designated for testing than any other Chinese cities, with 44 roads totaling 76 miles, ranging from city streets, rural backroads and expressways.

The plot below shows that in September and December, Beijing saw two bursts in open-road tests. It was during these two months that Beijing authorities issued batches of license plates.
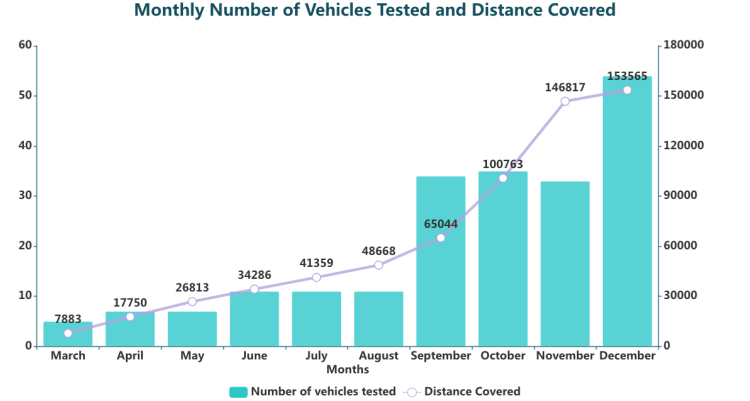
Table 2 below demonstrates that Baidu was the most active player, as it was doing open-road tests every month from March, when it got the first batch of five plates.
NIO did open-road tests in April, May, June, July, September, and October.
BAIC, a state-owned car maker received its first plate on April 25, 2018. It went on the roads from April to July but halted public testing afterwards.
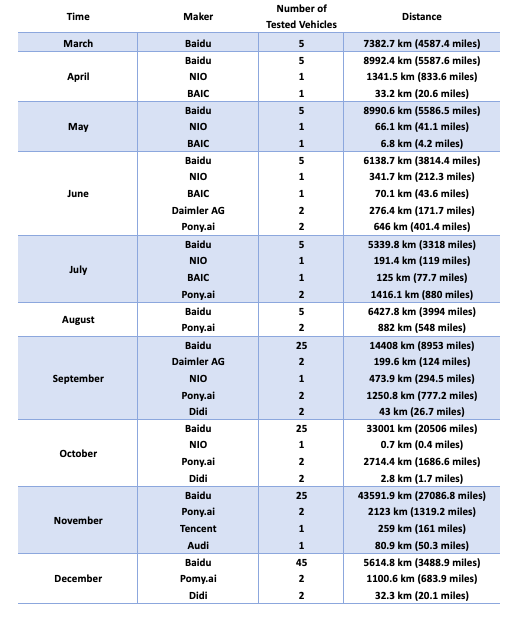
Pony.ai, a startup company focused on self driving software, tested from June all the way through December, making it the most active company in terms of public road testing after Baidu. Pony.ai announced on July 2, 2018 that it is the first startup company to have received testing license plates from the authorities.
Although Didi tested in three months, in September, October, and December, the distance it covered each time was short, of only a few tens of miles. The ride-hauling giant has been trying to ramp up the public tests, Didi told PingWest, and that it is building open-road test teams both in Beijing and the US.
Levels of Autonomous Driving
A set of broadly adopted standards in the international self driving community is called the SAE J3016 Levels of Driving Automation. This set of standards defined that there would be six levels of autonomous driving, from L0 to L5, where L0 represents complete human driving, and L5 represents that the car can drive itself under all conditions with no human safety/assistance needed.
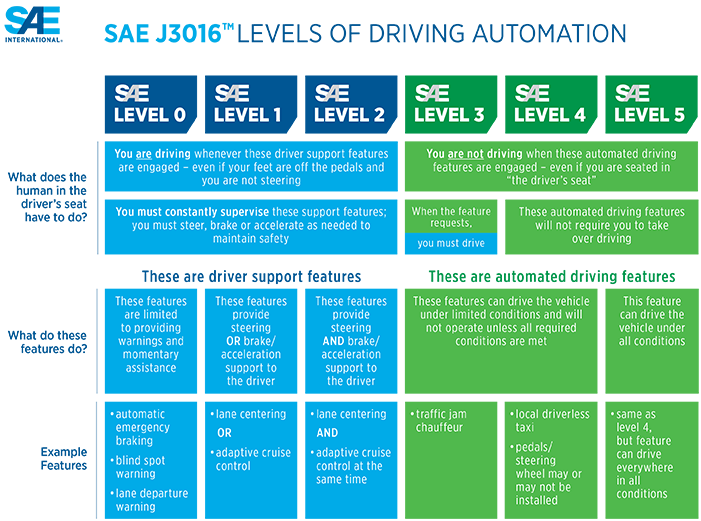
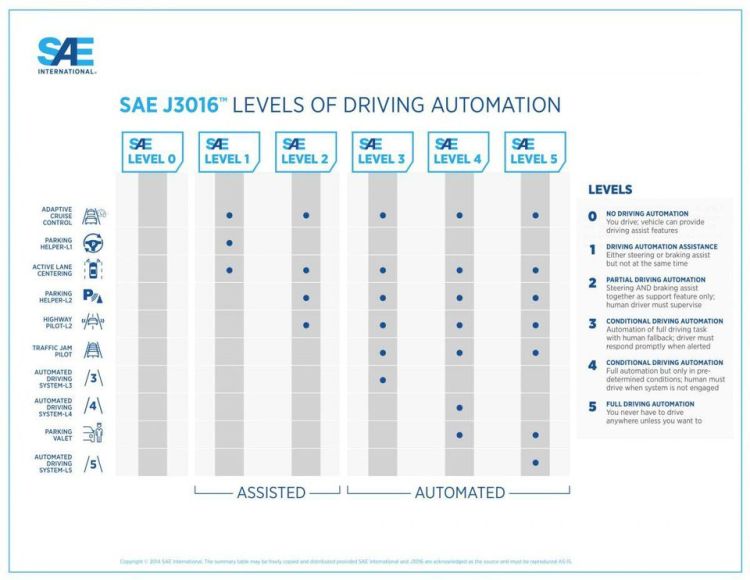
Companies with Chinese background, like their U.S. counterparts, have been adopting this set of standards. But in the mean time, Beijing authorities has also introduced its own system for self-driving tests, which added complexity to the situation.
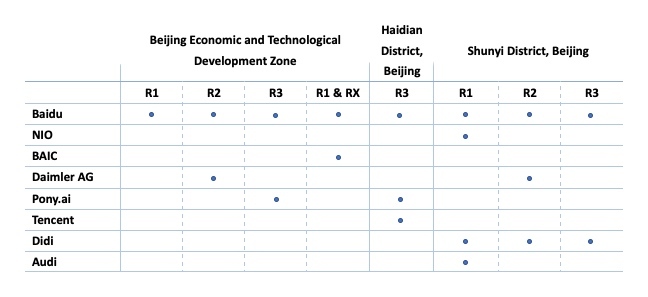
Based on the difficulties of tests, the Chinese government defined 5 levels of plates, noted as T1 to T5, and one special level, TX, referring to tests of v2x vehicles (vehicle-to-everything). Tests at a higher level include every testing hurdle at lower levels.
For example, a T1 level vehicle is able to obey traffic rules, including recognizing traffic signs, lines and lights, to accelerate, follow another car, change lanes, drive through crossings, make turns to left or right, etc. A T2 vehicle can do more, such as handling curved roads, make turns at crossings, etc. A T3 vehicle is able to make a U-turn at a crossroads. A T4 vehicle is able to pass other vehicles, park and parallel park. A T5 vehicle is able to drive in the fog, rain, etc., and pull over and stop to yield right of way to an ambulance, school bus, or other vehicles.
For an extra TX test, a vehicle will be tested on long-road vehicle-to-vehicle communication and at a crossroads.
According to Beijing, this additional system is there to better suit China’s conditions. In fact, the plates authorities issued mandate which level of testing companies are allowed to perform on their cars.
Since no company has demonstrated technology breakthrough with T4 potential, the highest level of plates issued was T3. Baidu and Pony.ai are the only two companies reaching that level.
But That's not all. The Chinese version also has another set of levels for different scenarios, from R1 to R5. Basically, R1 and R2 is two-way, four lanes with pedestrian crossings, signs and lights, low traffic flow, the usual city streets with difference in road straightness and quality. R3 consists of primary and auxiliary lanes, roundabouts and overpasses, while R4 adds tunnels and reversible lanes like the one on the Golden Gate Bridge. R5 will feature harsh weather and other special road conditions.
Baidu has covered R1-R3 roads in open-road tests. R3 also represents the highest level of driving scenarios a self driving vehicle in China can handle so far.
(Cover Image Credit: Sina)
